Normalizing the scaling of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is an essential step in comparing and evaluating the performance of different metrics within a balanced scorecard framework. Normalization allows you to standardize the KPI ratings and bring them to a common scale, enabling effective decision making and performance analysis. Here’s how you can achieve it:
- Define your KPIs: Start by clearly identifying the KPIs that are crucial for measuring the success of your business or project. These KPIs should align with your strategic objectives and reflect the key areas of performance you want to assess.
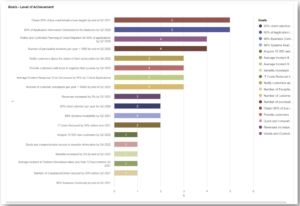
- Establish goals and targets: For each KPI, set specific targets that define the desired level of achievement. These goals should be realistic, measurable, and time-bound. They will serve as reference points for comparing actual performance.
- Determine rating scales: Assign rating scales or scoring systems to your KPIs. These scales will be used to assess the level of achievement for each KPI. The scales can be numeric (e.g., 1-10) or descriptive (e.g., low, medium, high) based on your preference and the nature of the KPI.
- Collect data and calculate ratings: Gather the necessary data to evaluate the performance of each KPI. This data can come from various sources such as financial statements, customer surveys, employee feedback, or operational reports. Calculate the ratings for each KPI based on the defined scoring system and the actual data collected.
- Normalize the ratings: Normalization involves transforming the KPI ratings to a common scale, allowing for meaningful comparisons across different KPIs. There are several normalization methods you can use, depending on the nature of your KPIs and the desired outcome. Some commonly used normalization techniques include:
-
- Min-Max normalization: This method scales the ratings between a minimum and maximum value, typically 0 and 1. The formula for min-max normalization is: normalized_value = (actual_value – min_value) / (max_value – min_value)
- Weighted normalization: In this approach, you assign weights to different KPIs based on their relative importance. The ratings are then multiplied by the corresponding weights before normalization to reflect their significance accurately.
- Compare normalized ratings: Once you have normalized the ratings for all KPIs, you can compare them directly, as they are now on a common scale. This comparison will provide insights into the relative performance of each KPI and help you make informed decisions based on the balanced scorecard analysis.
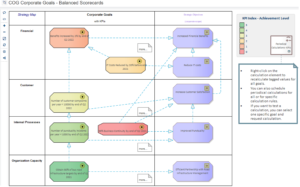
Labnaf rating normalizations are powered by the Labnaf cascaded value calculation engine.
Labnaf charts and dashboards are powered by Sparx Systems Prolaborate.